In the first part of the article Blow Molding and its types of processes were introduced. In other words, blow molding is the forming of a parison, which is embedded in the mold, by blowing air, and is performed by three extrusion, injection and injection stretch.
In the second part, we first discuss the plastics that are suitable for this type of molding, and then discuss the advantages and disadvantages of it.
Choosing the Right Plastic for Blow Molding Process
What features does a plastic need to be suitable for this type of molding?
To answer this question, we first need to know the two concepts of thermoplastic and thermoset. Polymers are divided into thermoplastic and thermosets, based on their type of heat behaviour. Thermoplastics are types that soften, melt, and return to solid state if they are cold (this can be done repeatedly), if they are heated. But in thermosets due to heat, a chemical reaction occurs that causes cross-links between the polymer chains and the hardened material to lose their ability to melt and thus their processability. That is why thermoplastics are used in plastic molding processes, such as blow molding, injection molding, compression molding, and so on. For example, nylon, polycarbonate, polyethylene, polypropylene and polybutylene, are thermoplastic and epoxy, polyimide and alkyd, are thermoset.
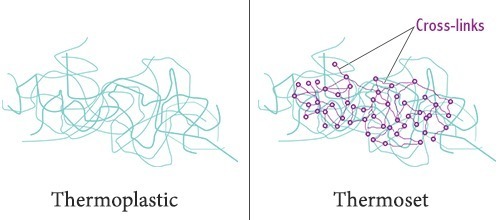 Figure 1. thermoplastic and thermoset polymer [4]
Figure 1. thermoplastic and thermoset polymer [4]Among the large family of thermoplastics, polyolefins, due to their properties, are used in a variety of molding processes, including injection molding, sheet extrusion, coating extrusion, and in particular blow molding. The advantages of polyolefin resins include their processability, toughness and good chemical resistance, light weight and relatively lower price than other plastics. In addition, the basic properties of polyolefins can be converted to a wide range of desired properties. These materials can be extruded with various other polymers. For example, ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH) and nylon are used to produce multilayer containers with gas permeability. Polyolefins used in blow molding are LDPE, LLDPE, MDPE, HDPE, ethylene copolymer such as ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), polypropylene and propylene copolymer. [2]
The major areas of application of polyolefins in the blow molding process are as follows:
- Food packaging, detergents, cosmetics and personal care
- Vehicle parts, such as fuel tank, oil bottle, air duct and seat
- Consumer products, such as toys, home appliances and sports goods

To answer this question, we will examine the concept of grade.
Grade
Plastics are classified by type of application by grade. In fact, grade shows what properties a plastic has and what it’s good for. For example, Table 1 shows the differences between the properties and application of several grades of polyethylene:
Table 1. Difference between properties and applications of somme grades of high density polyethylene [2]
| Grade | Property | Application |
| BL3 | High density and stiffness, good ESCR | blow molding; bottles, containers up to 2 L, packaging for pharmaceuticals and surfactants |
| I4 | flows very easy , high density, hardness | injection; lightweight home appliances, disposable parts, complex components |
| EX3 | good toughness, low gel point, good tear strength, good rigidity and adhesion, high molecular weight | film; packaging films and sheets |


The physical and mechanical properties of some grades of high density polyethylene and polypropylene are also presented in the following two tables.
Table 2. Physical and mechanical properties of different high density polyethylene grades [2]
| ISO | 1183 | 1133 | 179/1eA | 527 | 868 | |
| Grade | Process | Density (KJ/m2) | MFI (190°C/5kg), (gr/10min) | Impact strength (KJ/m2) | Yield stress (MPa) | Hardness (Shore D) |
| BL2 | Blow molding | 0.944 | 1.1 | 11 | 22 | 60 |
| EX3 | Pipe | 0.948 | 0.22 | 25 | 23 | 62 |
| I4 | Injection | 0.954 | 4 | 3 | 26 | 62 |
| EX$ | Film | 0.956 | 0.28 | – | 27 | 60 |

Table 3. Physical and mechanical properties of different polypropylene grades [3]
| ASTM | D1238 | D256 | D790 | D638 | |
| Grade | Process | MFI (230°C/2.16kg), (gr/10min) | Notched Isod impact strength (J/m) | Flexural modulus (MPa | Yield strian (%) |
| HP432C | Blow molding | 0.3 | 200 | 1350 | 34 |
| RP344R | Blow molding | 25 | 55 | 1100 | 10 |
| HP500P | Injection | 17 | 30 | 1550 | 12 |
| HA701T | Injection | 45 | 28 | 2050 | 6 |
Figure 6. Application of different grades of polypropylene [9]
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blow Molding
Blow molding like other forms of plastic molding, has its own advantages and disadvantages. some of which have been briefly mentioned in the previous article. The following table examines this in more detail:
Table 4. Advantages and disadvantages of blow molding processes [1]
| Process | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Extrusion | cheaper tools (30-40%) | low efficiency |
| Extrusion | high production rate | high pinch-off (5-40%), Especially in low volume containers) |
| Extrusion | produce hollow handle and wide-mouth containers | there is always the possibility of die lines or extrusion lines |
| Extrusion | coextrusion | trim is necessary to remove the tail |
| Extrusion | able to control weight | probability of “die swell” phenomenon |
| Injection &injection stretch | high efficiency (93-98%) | more expensive machinery |
| Injection &injection stretch | lowest off-fall (normally less than 1%) | limits in production of large volume containers |
| Injection &injection stretch | better control of wall thickness | the diameter of wide-mouth containers is limited |
| Injection &injection stretch | no pinch-off | the manufacturer does not have complete control over the temperature profile |
Sources
1. Samuel L.Belcher, practical guide to injection blow molding, CRC publication, 2007
2. http://v1.petrochem-ir.net/en/product/polymers?page=hdpe.htm
3. http://www.jppc.ir/
4. https://qph.fs.quoracdn.net/main-qimg-4985d7dfe92871d093accbcd60477942
5.https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/santa-barbara-additive-manufacturing-company-alt-llc-announces-upcoming-indiegogo-campaign-recycled-3d-printing-filament-from-everyday-plastic-waste-300375308.html
6.https://www.alibaba.com/product-detail/L501-virgin-hdpe-plastic-granules-pellets_62043686813.html spm=a2700.7724857.main07.33.3e531f9e92BLXT
8. https://shoraimandiri.wordpress.com/
9. http://chemical.milliken.com/blog-posts/reduce-reuse-recycle-the-core-of-milliken-s-sustainability-and-innovation
Compiled by: Hamidreza Tayari