Different Types of Polymer Adhesives

Different Types of Polymer Adhesives
Different Types of Polymer Adhesives
Adhesives have been used by humans for a long time, so that today they are an inseparable part of various industries. Today, with the growth of technology, polymer adhesives replace other sources of fasteners in various cases. In this article, different types of adhesives are introduced, the amount of adhesive consumption in different industries and in the world is stated, and its applications in different industries are examined [1].
Adhesive
Adhesive is a material which is used for keeping two surfaces together. Before, use an adhesive surface preparation must be done. For surface preparation, first of all adhesive must wet the surface, then after applying the adhesive on the surface, it must lead to strength between surfaces and remain stable. Most of the times the raw materials which are used for adhesives, are polymeric materials. These polymers can be categorized as below [2]:
1. Thermoset Adhesives:
• Epoxy resins
• Phenolic resins
• Amine resins
• Polyurethanes
• Silicone resins [3]
2. Thermoplastic Adhesives:
• Poly vinyl acetate
• Poly vinyl acetal
• Poly acrylate
• Cyanoacrylate
• Cellulose derivatives
• Melt thermoplastic adhesives (Thermal adhesives) [4]
3. Rubber Adhesives:
• Nitryl rubber
• Neoprene
• Polysulfides [5]
4. Natural Adhesives:
• Herbal
• Animal glue [6]
Applications of adhesives in different industries
Adhesives are extremely used in the most of industries such as: food packing, drug packing, construction, automotive, and medical. As it can be seen in figure1, most of the use of adhesives belongs to packing industry [7].
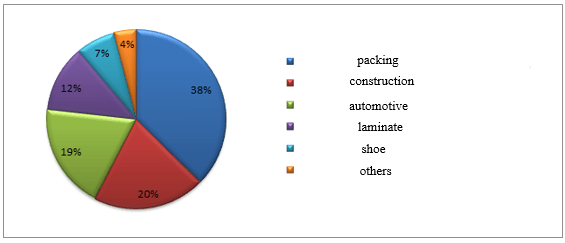
Fig. 1. Applications of adhesives in different industries [7]
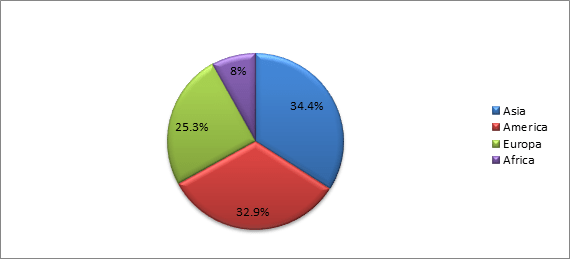
Fig. 2. Consumption of adhesives in the world [8]
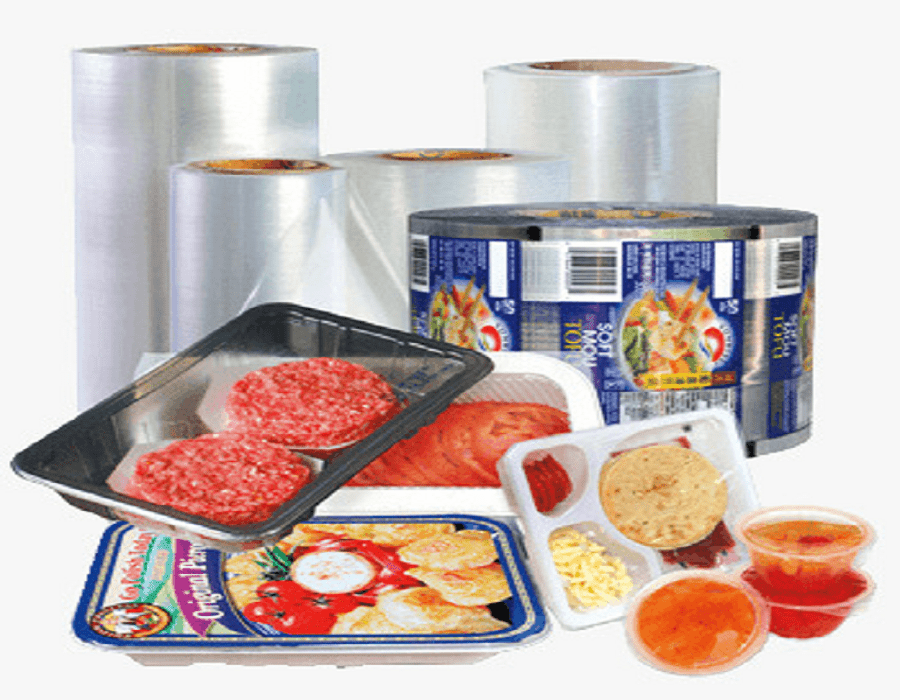
Uses of adhesives in the packing industry includes: Multilayers films, Labeling, and food packing
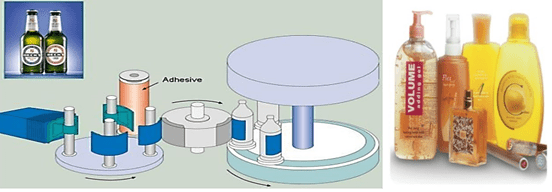
Fig. 3. Labeling on the bottles process [9]

Fig. 4. Use of adhesive in multilayer food packing [9]
Uses of adhesive in automotive industry
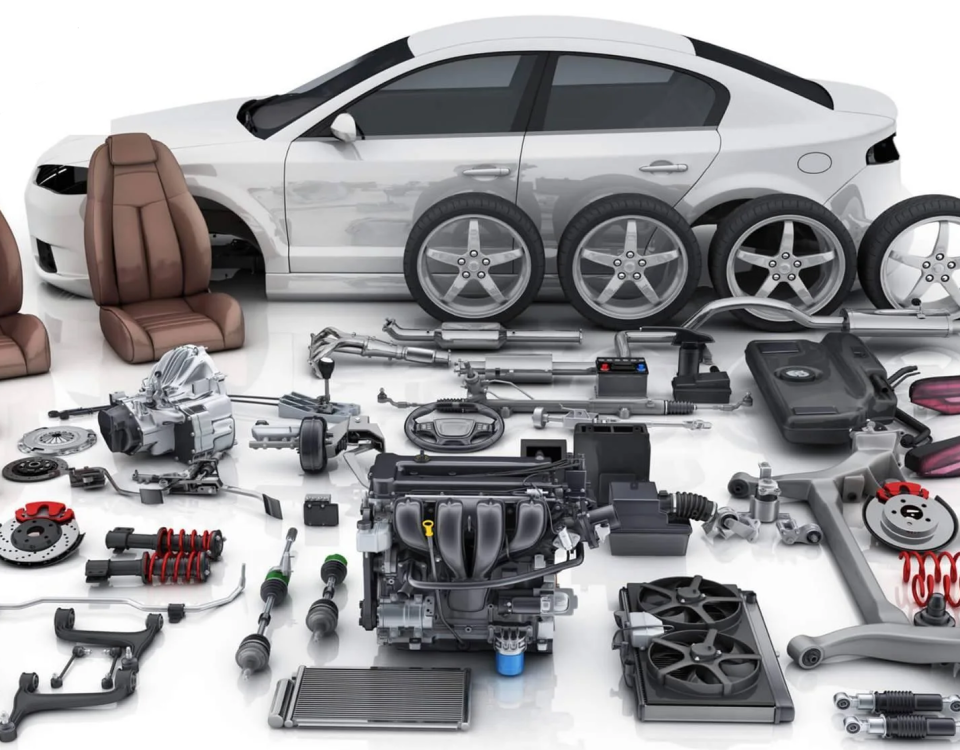
As it can be seen in the figure 5 to link different parts such as: roof, windshield and, side panels are sued adhesives.
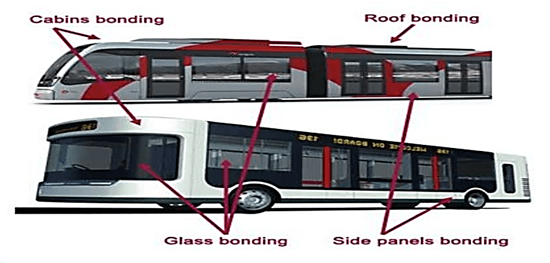
Fig. 5. Adhesives applications in automotive industry [10]
Adhesives applications in transportation industry
Nowadays, in transportation industry especially in marine transportation is adhesives are widely used because, in marine industry the low weight of products and improving the quality of products is crucial. In figure 6 and 7 use of different adhesives in the ships and aircrafts has shown.
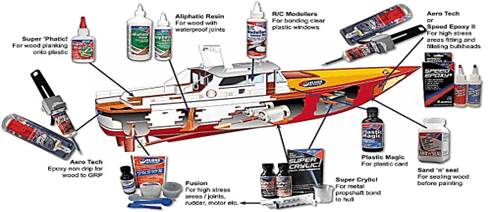
Fig. 6. Adhesives uses in the ships [11]

Fig. 7. Adhesives which are used in an airplane [12]
Adhesives in Construction
It can be used for:
• Gluing ceramics and tiles
• Gluing flooring
• Gluing prefabricated and concrete roofs
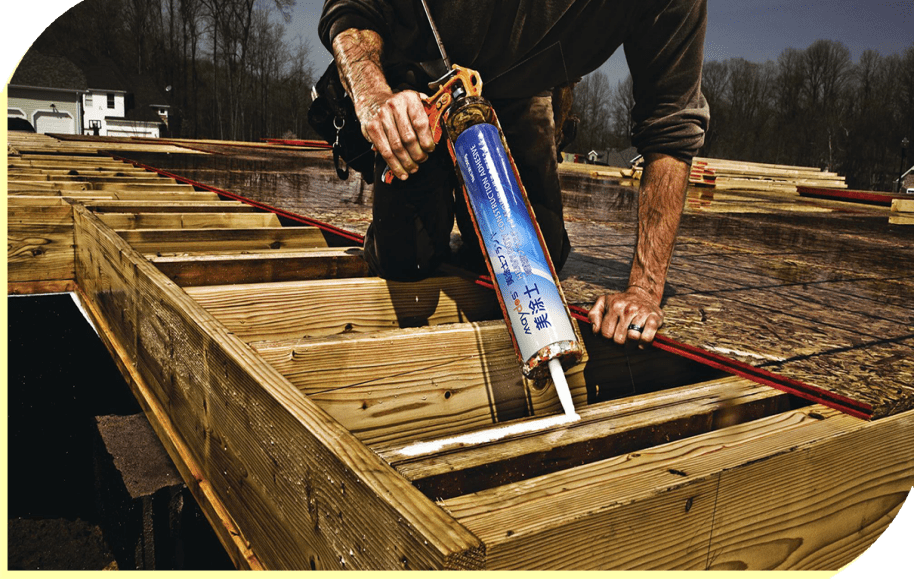

Fig. 8. Uses of adhesives in construction [13]
Another way to classify adhesives is based on their curing method, based on which adhesives can be divided into two categories:
1. curing adhesives without the need for an initiator:
• Dry adhesives
• Hot melt adhesives
• Pressure-sensitive adhesives
• Interlayer adhesives
2. curing adhesives with the help of initiator:
• Adhesive curing under UV
• Adhesive curing by heat
• Adhesive curing by humidity
Emulsion Adhesives
There are adhesives that are cured and hardened by drying. These adhesives are classified into two categories: water-based and solvent-based, which are called emulsion adhesives.
Solvent-based adhesives are divided into two categories:
1- Wet bonding adhesives
2- Contact adhesives
Water-based adhesives are adhesives that use water as an active component, and the connection is made by water evaporation or water absorption by the base material. Water-based adhesives, like solvent-based adhesives, are divided into two categories: contact and wet bonding. It is expected that water-based adhesives will replace solvent-based adhesives in the last decade.
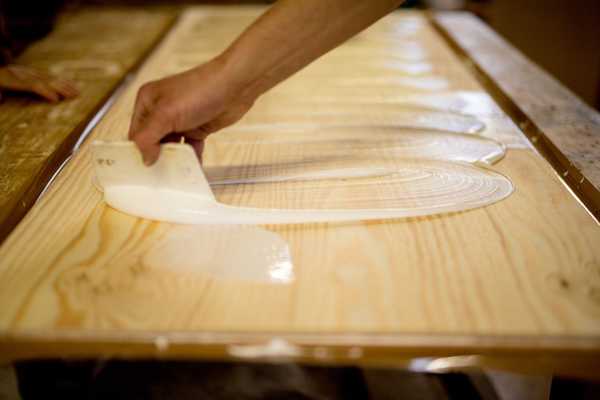

Fig. 9. Application of emulsion adhesives in the field of wooden joints, flooring installation, parquet, and packaging industry [14]
It is expected that in 2018, Hot-melt adhesives will have the largest proportion of consumption among all types of adhesives in various industries, including the packaging industry and non-woven textiles.
There are different types of hot-melt adhesives that are used in different fields, such as: Hot-melt adhesives based on polyolefin (polyethylene and polypropylene) in the packaging industry. Hot- melt adhesives based on polyvinyl acetate in the field of binding. Hot-melt pressure sensitive adhesives used in the field of health and medical products. Hot-melt adhesives in the automotive and filter industry.

Fig. 10. Applications of hot-melt adhesives [15]
Pressure Sensitive Adhesives (PSA)
Pressure-sensitive adhesive is an adhesive that adherence the adhesive with the substrate by applying a small amount of pressure. Pressure-sensitive adhesives can be solvent-based, water-based, or hot-melt.

Fig. 11. PSA Adhesives [16]
Polymers which are used as PSA adhesives: Polyester, Polyurethane, Silicone, and Acrylic.
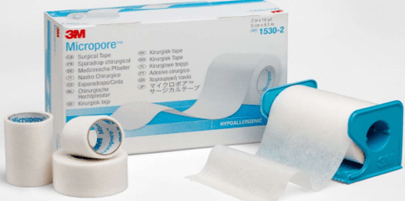
Fig. 12. PSA Adhesives in the production of hypoallergenic adhesive [17]
UV Adhesives
Adhesives that are cured with UV rays, this curing method requires less time than the thermal method and reduces the side products, so that UV adhesives have replaced thermal adhesives in most fields. UV adhesives are used for medical purposes such as making syringes, tweezers, and dental fillers. These adhesives are also used in the wood industry, making decorations, and other industries.
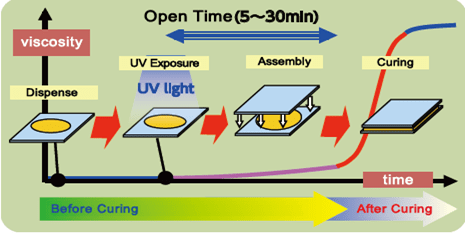
Fig. 13. Curing mechanism of UV adhesives [18]
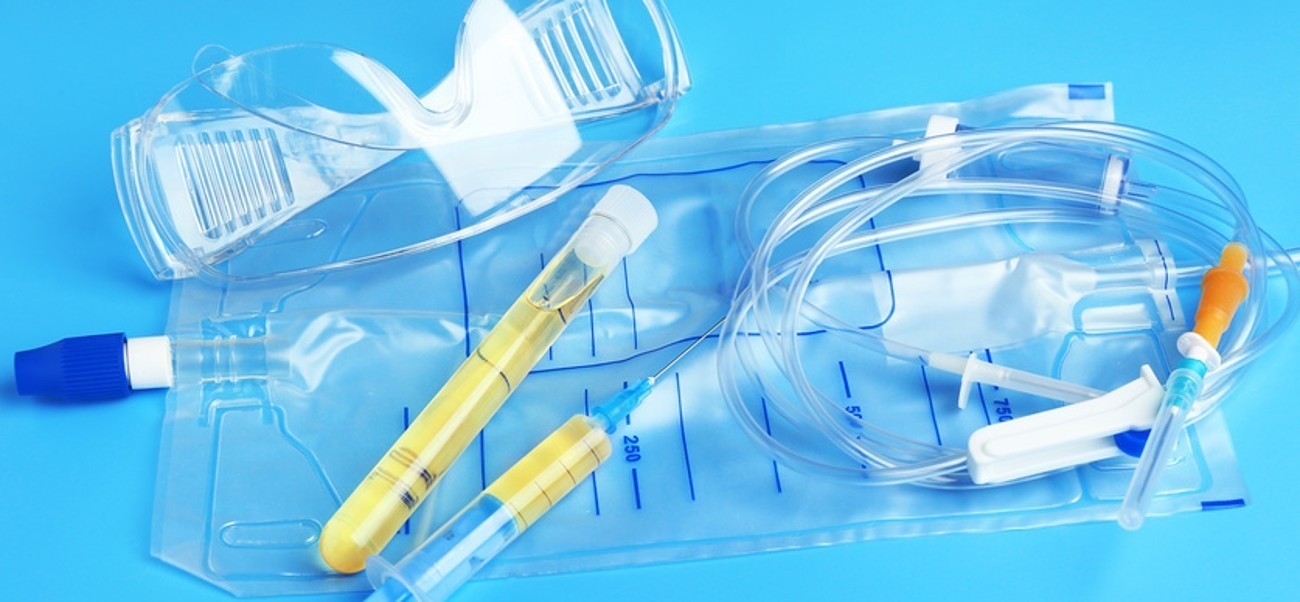
Fig. 14. Medical applications of UV adhesives [19]
Henkel of Germany
3M of USA
HB Fuller of USA
Bayer of Germany
Mactac of USA
Author: Emad Izadi Vasafi
References:
[1] https://polymerdatabase.com/Adhesives/Adhesives.html
[2] https://www.britannica.com/technology/adhesive
[3] https://fastenerengineering.com/what-are-thermoset-adhesives/#:~:text=Thermoset%20adhesives%20are%20thermosetting%20polymers,such%20as%20heat%20or%20light.
[4] https://www.labelplanet.co.uk/glossary/adhesive-thermoplastic/
[5] Pocius, A. V. “Adhesives and sealants.” (2012): 305-324.
[6] https://blog.lddavis.com/natural-glues-for-industrial-applications
[7] https://www.masterbond.com/industries/adhesives-sealants-and-coatings-variety-industries
[8] https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/adhesives-and-sealants-market-101715
[9] Gadhave, Ravindra Vilas Indubai, and Chaitali Ravindra Gadhave. “Adhesives for the Paper Packaging Industry: An Overview.” Open Journal of Polymer Chemistry 12.2 (2022): 55-79.
[10] https://www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2018/01/11/1287163/0/en/Automotive-Adhesives-and-Sealants-Bonding-for-Betterment-of-Automobile-Industry-to-Witness-a-CAGR-of-7-9-during-2017-2023.html#:~:text=Automotive%20adhesives%20and%20sealants%20are,mechanical%20bolts%2C%20welds%20and%20rivets.
[11] https://www.adhesivesmag.com/articles/97993-marine-applications-for-adhesives-and-sealants
[12] https://market.us/report/aerospace-adhesives-and-sealants-market/
[13] https://mccoymart.com/post/what-are-the-applications-of-adhesives-in-the-construction-industry/
[14] https://www.fcimag.com/articles/92241-all-about-flooring-adhesives-chemistries-and-applications
[15] https://www.asahimelt.com/eng/hm/
[16] https://onlytrainings.com/psa-pressure-sensitive-adhesives-formulation-optimization-and-key-ingredients-selection-for-high-performance-applications
[17] https://kmsmedsurg.com/3M-Micropore-Surgical-Tapes-with-Dispenser?language=en¤cy=USD
[18] Sanai, Yasuyuki, and Kouzou Kubota. “Effect of UV-curing conditions on the polymer structures: A comparison between coating and adhesive.” Polymer Journal 52.9 (2020): 1153-1163.
[19] https://www.heraeus.com/en/hng/industries_and_applications/uv_technology/curing_of_uv_adhesives_and_uv_paints_in_medical_engineering.html



