Controlled Rheology Polypropylene (CRPP)
Aria Polymer Controlled Rheology Polypropylene (CRPP), known as Aria Add 2440 and Aria Add 2440T136 are formulated for PE and PP products. These masterbatches cover a wide range of applications such as melt blown, melt spinning, injection molding, extrusion coatings, thermoplastics reinforcement, recycling and compounding industry. Aria Add 2440 and Aria Add 2440T136 can increase PP MFI and also decrease PE MFI, depending on the intended use. By means of Aria Add 2440, melt and rheological behavior can be optimized without a change in transparency, odor or etc.

The polypropylene produced in conventional reactors has excellent mechanical properties but due to its linear structure, high molecular weight and wide molecular weight distribution, it has high melt viscosity and elasticity, resulting in low melt strength.
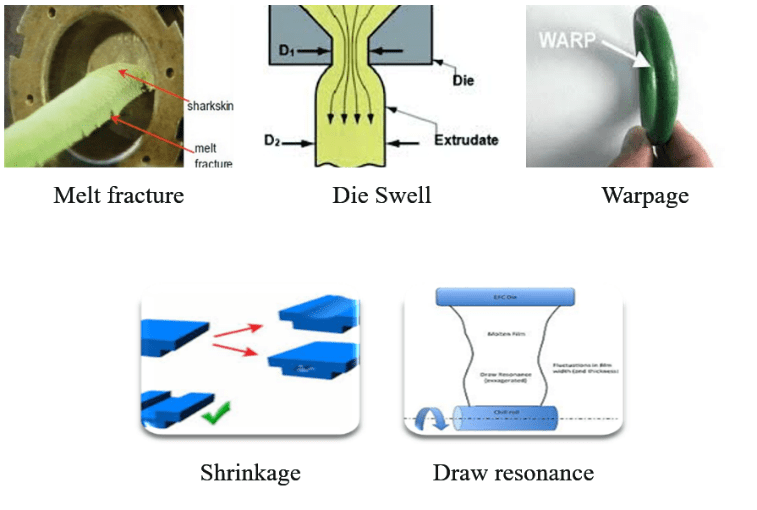
As a result, the use of polypropylene derived directly from polymerization, causes problems such as melt fracture, draw resonance, die swelling and dimensional instability, in routine extruder applications such as spinning or injection molding to produce thin-walled components. Some of these problems are shown in this figure:
Consequently, reforms are needed to increase the melt flow index and improve the polymer melt behavior.
Since the control of molecular weight and its distribution during the polymerization process is not economically advantageous, properties modification methods can be used in the reactive extruder. The use of MFI modifier additive is one of the frequent methods to increase PP melt index.
MFI- modified polypropylene is used in film, fiber, injection molding, extrusion coatings, glass mat and long fiber-reinforced thermoplastics, PP recycling and compounding industry.
The Controlled Rheology Polypropylene (CRPP) can be used to adjust the MFI of PE in recycling and compounding industry. The presence of MFI modifier additive causes the macro radicular bonding, which results in a decrease in the melt flow index, slow relaxation and change in mechanical properties, in particular, an increase in impact strength and a decrease in polyethylene elongation. For better processability of PE in blown molding and extrusion foaming, it is desirable that the material has a lower cutting speed, high viscosity complex and longer relaxation time.