Modern composite coatings in repair of oil and gas pipelines

Modern composite coatings in repair of oil and gas pipelines
Modern composite coatings in repair of oil and gas pipelines with the capability of use in marine and onshore environments
Introduction
Nowadays, due to the importance of maintenance of oil and gas pipelines, new methods have replaced old mechanical and traditional methods such as complete replacement of pipelines or welding that require high cost and very difficult installation operations, along with many risks of life and financial. Therefore, repair of pipelines using composite walls, which are mainly done through manual layering in the pipes or complete baking of composite walls (spring clock), has increased day by day, these methods also cause problems such as lack of proper adhesion, dirt of the place, etc. due to the variety of weather in the crossing of the lines. Oil and gas transmission pipes have increased the importance of manufacturing composite coatings with the ability to use concurrently in On Shore and Off Shore environments and their quick and easy installation, so the world’s major companies have conducted extensive research on the construction of composite walls by pre-impregnated method with the least environmental pollution and high flexibility to install at any level, especially in underwater environments. They did. In the new generation of composite coatings, innovation is in its flexibility and prefabricated, which makes it possible to use it at different levels and conditions.
According to a 2014 report by the North American Center for Oil and Gas Pipelines, the life of more than 60 percent of oil and gas pipelines worldwide is projected to be over 40 years old because these worn-out pipes have problems such as explosions, leaks, etc. Efforts to repair these pipelines in North America, where three of the six countries with the highest oil and gas pipelines are located, were the explosion caused by a spill of oil pipelines in the San Francisco suburbs that killed and injured 128 people and destroyed thirty-eight homes, paying attention to the issue of repairs of the oil and gas pipelines. Therefore, nowadays, due to the high volume of oil, gas and petrochemical activities in the world and the desperate need for repairs of transmission pipelines, considering the economic importance of these products, repairs of oil and gas pipelines are one of the concerns of major industries and international oil companies in the world.
The first methods in repairing oil and gas pipelines, old mechanical and traditional methods such as pipeline replacement and later welding metal steel method, due to high costs and very difficult installation operations, along with the risks of life and financial damage caused by explosion during repairs, have a very high risk. Therefore, pipeline repair was replaced by mechanical and traditional methods using pipeline repair composite wrap technology. This technology, which is carried out using composite coatings, was very welcomed in the world because it does not require the pipeline to be removed. This technology is mainly done through two methods of manual layering at the hand lay-up site or the complete baking of composite coatings at the factory site, which was invented by Clock Spring Company. These methods also cause problems such as lack of proper adhesion, filth of the place, lack of skilled workforce, etc. during installation of the wall. On the other hand, due to the variety of climate of the crossing site of oil and gas pipelines, the construction of composite coatings with the capabilities of concurrent application in On Shore and Off Shore environments and their quick and easy installation has increased, which is using manual layering methods in the repair site of the pipes (Hand-lay-up), or complete sintering of composite coatings at the factory site are difficult or unworkable. Therefore, the world’s major companies have conducted extensive research on the construction of composite walls in a pre-impregnated manner with the least environmental pollution and high flexibility to be installed at any surface, especially in underwater environments
In the new generation of composite coatings, innovation is in its flexibility and prefabricatedness, which makes it possible to use it on different surfaces and conditions. In the pre-impregnated process which is done with specially designed devices, the reinforcing fibers are impregnated with resin, but by applying certain baking conditions, the resin is partially cooked which leads to the formation of composite form due to the lack of complete resin cooking. In this method, by exposing the composite wall to moisture or UV light, the composite wall is cooked in a very short time and this method is the only molding method of composites that has the ability to use at the same time in aquatic and dry environments, it is worth mentioning in these coatings, using technology to improve the physical and mechanical properties of the composites with the aim of reducing the weight of the product and controlling the duration of the product. And the amount of pre-impregnated gelling is done.
Methods
As mentioned in the history of technology section, currently, due to numerous problems that traditional mechanical methods including pipe replacement and welding of metal sleeves in the repair of oil and gas pipelines have created, various technologies in the production of composite coatings for repairing oil and gas pipelines have replaced traditional mechanical methods. These technologies include:
- Complete cooking method in the factory
- How to bake at the pipe repair site
- Pre-impregnated method
So how each product is produced will be as follows:
Curing technology at the pipe repair site
Reinforcing fibers (usually glass fibers) are soaked by liquid resin at the repair site of the pipes and then soaked on the pipe (manual layering method). After applying composite coating on damaged pipelines, with baking conditions, the composite is formed and tightened.
 Figure 1. Curing technology at the pipe repair site
Figure 1. Curing technology at the pipe repair site
Complete curing technology in the factory
Composites, which include reinforcing fibers and polymer thermoset resins, are cured with common methods of forming composites at almost complete production stage and composites are produced in the factory. These composite coatings produced in diameters slightly less than the outer diameter of the damaged pipes are wrapped and wrapped around the pipe when applied on the composite casing pipe and wrapped by layer-by-layer glue around the pipe. This technology was invented by Clock Spring under the same title.
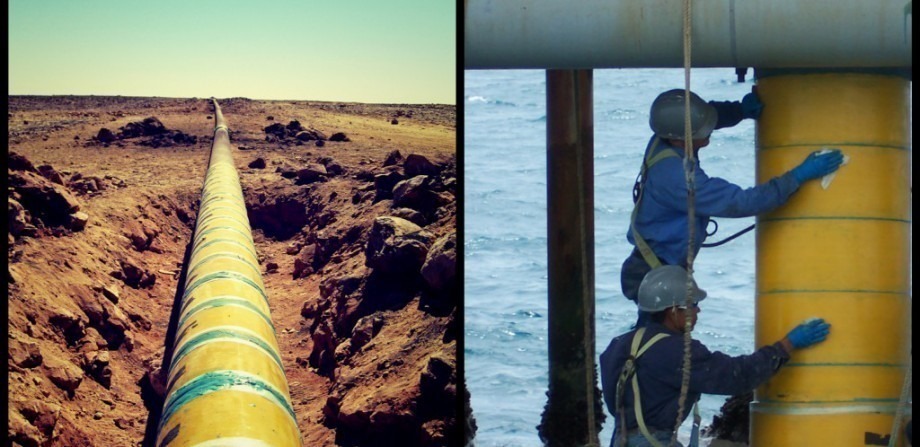 Figure 2. Complete cooking technology in the factory
Figure 2. Complete cooking technology in the factory
Pre-impregnated technology
Reinforcing fibers are soaked with a certain percentage of resin and are semi-baked. Then, this pre-impregnated composite is baked and molded during use by applying special conditions such as UV light, heat or humidity in a short time.
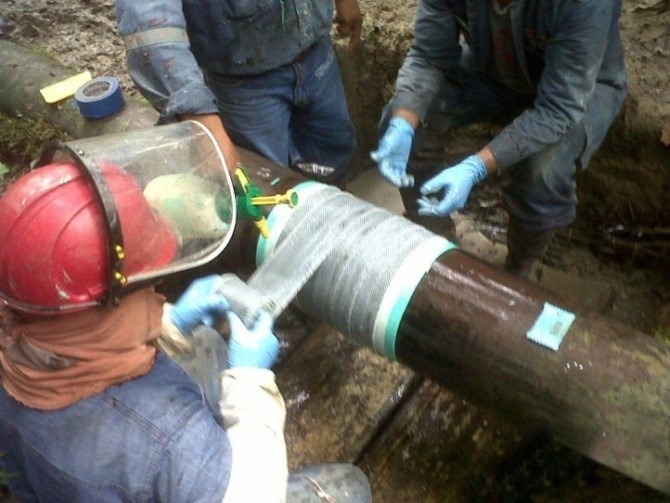 Figure 3. Pre-impregnated technology
Figure 3. Pre-impregnated technology
In order to investigate the status of pre-impregnated technology and compare it with other common technologies in repair method with composite coatings, the following table has been adjusted.
Table 1. Comparison of common technologies in the manufacture of composite coatings for repair of oil and gas pipelines
| Method Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Complete cooking method in the factory |
– Controlling the direction of fibers and percentage of resin and fibers – Removing the adjustment of variable parameters with the outer diameter of the pipe – Better and more uniform mechanical properties – High speed of applying composite coating after accurate measurements of pipe dimensions and damage – Clean process |
– Requires accurate measurements and expert force before applying the coating – Inability to apply on surfaces with irregular shapes or pipes with low diameter – No changing the size and diameter of the coating in case of any changes in the conditions of the damaged pipe |
| How to bake on-site |
– Ability to determine and change the amount and length of composite coating in place – Ability to repair pipes with non-regular shapes, T-shaped pipes , fittings, flanges and valves – No need for accurate measurements before applying the coating – Time and sintering process as a broadcast of coating installation operations – Cheap price |
– By changing the environmental conditions of the pipe, the amount of resin consumed, the cooking conditions change – The construction of the wall and its actions requires expert forces – Dirty process – High consumption of resin |
| Pre-impregnated method |
– Precise control of fiber percentage – Controlling the thickness of the layers – Reduce labor costs – Clean process – Higher quality – Higher flexibility compared to the complete production method in the factory |
– Requirement for special machine for composite production –Technical Special Hi-Tech – Requiring special storage conditions in order to prevent early cooking |
Fabrication of pre-impregnated composite
In the first stage of the construction of the mentioned composite, in the pre-impregnated process, which is done with specially designed devices, the reinforcing fibers are impregnated with resin, but by applying certain baking conditions, the resin is partially cured, which leads to the formation of composite form due to the lack of complete resin curing. This pre-impregnated composite wall can be placed in certain packaging’s until its service, and when needed, this composite wall is easily completed and hardened under moisture, and a composite wall with mechanical properties such as other walls will be achieved. In this method, by exposing the composite wall to moisture, the composite wall is cured in a very short time and this method is the only molding method of composites that has the ability to be used at the same time in aquatic and dry environments.
As mentioned below, the price of raw materials of traditional products (buying metal sleeves and tubes for replacement) is lower than the purchase price of composite coating raw materials. The final costs of mechanical repairs due to the costs of waste of oil or gas materials, the need to stop, the high cost of manpower due to the high duration of repair and high machine costs, are higher than composite coating methods.
Also, one of the most important factors in valuing products is the added value that creates added value for the main customer of this product, i.e. oil and gas pipeline maintenance company. In addition to the topic of competitive analysis of composite coatings, the example of the created value added of composite coatings in comparison with traditional methods in repairing oil and gas pipelines is discussed.
In a report from the Natural Gas STAR Center of America, a comparison was made between the costs of repairing gas pipelines in two traditional ways of replacing the pipeline and repairing with composite coatings on gas pipelines with a diameter of 24 inches for a length of 6 and 234 inches equivalent to 15 and 594 cm, as shown in the diagrams below.
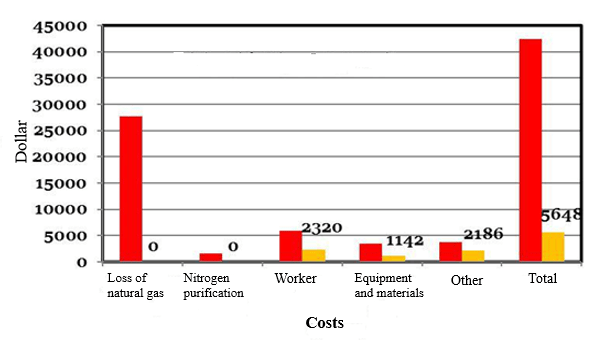 Figure 4. Comparison of repair costs of two methods of pipe replacement and composite coatings for 6 inches of pipes with a diameter of 24 inches
Figure 4. Comparison of repair costs of two methods of pipe replacement and composite coatings for 6 inches of pipes with a diameter of 24 inches
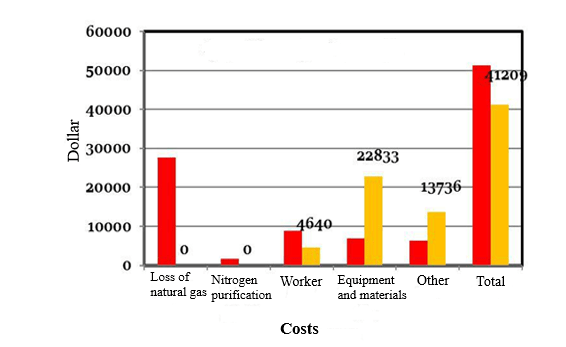 Figure 5. Comparison of repair costs of two methods of pipe replacement and composite coatings for 234 inches of pipes with a diameter of 24 inches
Figure 5. Comparison of repair costs of two methods of pipe replacement and composite coatings for 234 inches of pipes with a diameter of 24 inches
As mentioned in the diagrams above, a major share of the costs of repairs belonging to gas waste and the cost of human resources are needed in such a way that repairing gas transmission lines by composite coatings for meters less than 3 meters, between 10 and 20% of the repair cost will be replaced by a replacement method, this ratio of costs for meters above 3 meters will be between 75 and 85%. In order to repair 6 meters of pipe with a diameter of 24 inches (about 61 cm) the amount of about 350 million Rials is calculated the difference in costs of the two methods.
Conclusion
Common methods are used in repairing oil and gas pipelines, among which traditional methods of welding metal sleeves and replacement methods due to high overhead costs, life and financial risks and their incompleteness are being analyzed gradually. In composite methods that are used in three ways, complete baking in the factory, baking method at the pipe repair site, the pre-impregnated method is used.
Author: Emad Izadi Vasafi



