Plastic and Rubber Parts of the Automobiles

Plastic and Rubber Parts of the Automobiles
Since the beginning of the automotive industry, many changes have been made in automotives. Cars, vans, public transport vehicles and trucks are constantly updated to improve their performance. Steel and aluminum are the main materials in the automotive industry, and then polymers are widely used there. The use of polymers in the automotive industry has increased over time, and polymers have replaced metal parts in cars, which causes reduction in production costs, vehicles weight, fuel consumption, and thus CO2 emissions. In this article, we will discuss the plastic and rubber parts of the Automobiles [1].
One of the cases is replacing polymer parts with metals in car bumpers. Figure 1 illustrates this replacement.
 Figure 1- a car built in the 1990s and a car currently in production
Figure 1- a car built in the 1990s and a car currently in production
Engineering plastics, elastomers and foams are polymer materials used in the automotive industry.
Engineering Plastic Parts of the Automobiles
Plastic materials are polymers that can be shaped or molded, usually by applying heat and pressure. These materials are made from a wide range of synthetic and semi-synthetic polymer compounds that are ductile and therefore can be molded into any shape. The low weight, flexibility and high quality of plastics make them suitable for the automotive industry, reducing the overall weight of cars and leading to lower fuel consumption.
Typically, plastics are used in exterior parts such as body panels, bumpers, and fenders, and in interior parts such as dashboards, door panels, steering wheels, and decorative parts (Figure 2).
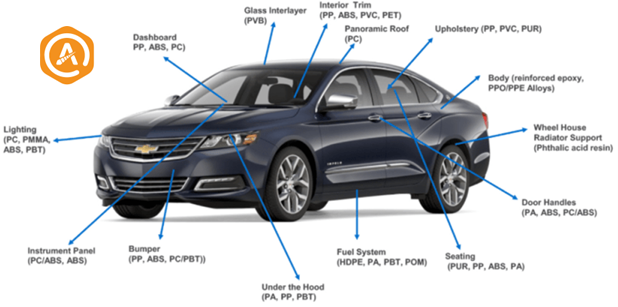 Figure 2- Plastics used in cars
Figure 2- Plastics used in cars
Polymers used in plastic parts of cars include:
- Polypropylene
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Polyvinyl chloride
- Polycarbonate
- Polyethylene
Polypropylene
Polypropylene is the most widely used plastic in automobile manufacturing, and as a thermoplastic polymer, it can be molded into any desired shape. This polymer has very high chemical and thermal resistance and shows very good impact resistance. Polypropylene is found in the exterior of the car, often in the front and rear bumpers and in the interior of the cabin in the floor of the car. Also, compared to other plastics, it is a more suitable option for expensive plastics with similar strength and durability, which reduces production costs.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
The use of ABS polymer provides a final product with a glossy appearance. Dashboard and steering wheel covers are often made of ABS plastic. It can also be used for car body parts. Plastics used in cars, such as ABS, cause absorb and dissipate energy during an impact to the car body, keeping passengers safe.
Also, another of its applications in engineering plastics is in the form of complex copolymers; That is, 15% of glass fibers reinforced with ABS copolymer and styrene grafted with maleic anhydride (GF-SMA), is made into a compound and used in the automatic roof of cars. Some automotive companies also use a mixture (SMA-GF) and ABS and glass fibers.
 Figure 3- Automatic roof in the car
Figure 3- Automatic roof in the car
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
It is a flame-resistant plastic that exists in two forms, flexible and hard. PVC is another common plastic that used in cars due to its ductility and glossy cover. Rigid PVC is often used to make dashboards and car body parts.
 Figure 4- Glossy PVC coating on the body
Figure 4- Glossy PVC coating on the body
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is impact resistant and is often used in car bumpers and headlight lenses. This type of plastic has a good resistance to atmospheric factors and different weather conditions, i.e. rain and snow, heat and cold, do not disturb its performance. Polycarbonate is lightweight, thus reducing overall vehicle weight, which in turn improves vehicle efficiency and fuel economy [2].
 Figure 5- Front and rear bumper of the car
Figure 5- Front and rear bumper of the car
Polyethylene
Metal-polymer-metal structures, such as aluminum (Al)-low density polyethylene (LDPE) panels, have gained importance in automotive applications due to their light weight and energy dissipation properties. These structures produce new car parts with good mechanical properties. These structures produce new car parts with good mechanical properties [1].
Elastomers
Rubber is a flexible and elastic polymer that can be found in both natural and synthetic forms. Natural rubber is the elastic material obtained from the sap of the Hevea tree (figure 6).
 Figure 6- Natural rubber is obtained from the sap of the Hevea tree
Figure 6- Natural rubber is obtained from the sap of the Hevea tree
Because of their resistance to heat build-up, natural rubbers are widely used in racing cars, airplanes, trucks, and buses. The distinctive characteristics of tires such as high strength and resistance to tearing while being flexible have highlighted their role in the automotive industry.
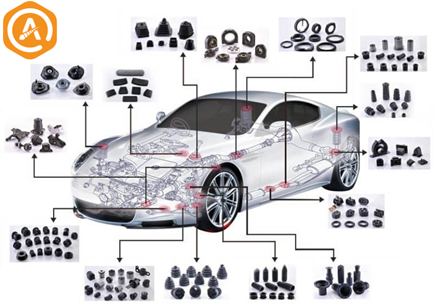 Figure 7- Rubbers in different parts of the car
Figure 7- Rubbers in different parts of the car
Rubbers are a group of elastomers that have significant flexibility due to the presence of cross-link in their structure. Rubber parts are present in various parts of the car, some of which are mentioned.
-
Tires
Most of the tires include natural rubber and styrene butadiene rubber. After that, poly-cis butadiene rubber and butyl rubber are added with a smaller percentage.
-
Vibration Dampers
Polyurethane elastomer, neoprene, olefin rubber, silicone and fluorocarbon are used in their construction. Semi-flexible polyurethane foams are also used in some parts.
 Figure 8- Components in anti-vibration systems
Figure 8- Components in anti-vibration systems
-
Sealants
All types of olefin rubber, natural rubber, styrene butadiene rubber and polyurethane elastomers are used. Polyurethane glue is generally used to bond them to the car body. Also, most USA car manufacturers use one-component moisture-curable polyurethane sealants to bond windshields and rear windshields to car bodies.
 Figure 9- Sealants in the car
Figure 9- Sealants in the car
-
Gaskets
Their raw materials are thermoset polyurethane resins, olefin rubber, neoprene and styrene butadiene rubber.
 Figure 10- Rubber gaskets in the car
Figure 10- Rubber gaskets in the car
-
Car belts
These parts are also made of polyurethane elastomers.
 Figure 11- Car belt
Figure 11- Car belt
-
O-rings
 Figure 12- O-rings used in cars
Figure 12- O-rings used in cars
-
Radiator hoses
Olefin rubbers are used in this section, because they can be used in different weather conditions [3].
Polyurethane foam Parts of the Automobiles
These foams have different types and are used in different parts of the car.
1-Rigid foams
Their density ranges from 0.5 and 1.5 lb/ft3 and are used to barrier corrosion and body sound absorptions.
2- Semi rigid Foams
These foams have very good shock and impact absorption properties, which makes them used in car dashboard panels and seat cushions.
3- Semi flexible Foams
Semi-flexible Foams consist of microcellular urethanes. High compressibility, small lateral expansion, and resistance to abrasion and environmental stresses make these materials ideal for many seal applications. higher-density grades are used in the motor base and handle, because they have sound and vibration insulation properties.
4- Flexible Foam
Flexible urethane foams are used for automotive cushioning and upholstering furniture. These foams have high strength against high weights, on the other hand, their weight is less compared to the old fibers used in the past [4].
 Figure 13- Foam used in car seats
Figure 13- Foam used in car seats
References
[1]. Vieyra, Horacio, et al. “Engineering, recyclable, and biodegradable plastics in the automotive industry: A review.” Polymers 14.16 (2022): 3412.
[2]. https://www.acplasticsinc.com/informationcenter/r/plastic-used-in-cars.
[3]. Walter, G. “Elastomers in the automotive industry.” Rubber Chemistry and Technology 49.3 (1976): 775-822.
[4]. Szycher, Michael, ed. Szycher’s handbook of polyurethanes. CRC press, 1999.



