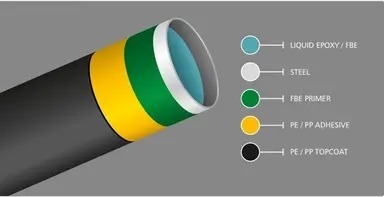
The Solution for Compatibility in Multilayer Packaging Films; Tie Layer Adhesives

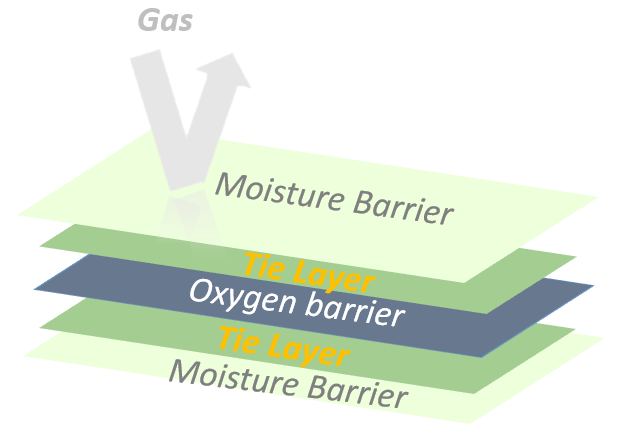
Multilayer films with a special structure based on Fig.1 have been used in food packaging recently. These films are designed to protect food for a long time by avoid permeating gases such as oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapor. The gas barrier ability is resulted by combination polar and non-polar polymers. However, the challenge of poor adhesion between incompatible polymers would solve by using a particular type of adhesives: “tie layer”
In food packaging, heat and chemical stability, barrier functionality, mechanical strength and optical properties are determining factors. Basically, plastics are widely used for food packaging since their advantages such as processability, mechanical strength, chemically inert, cost efficiency, lightweight, transparency, heat resistance and barrier properties. Generally polyolefin polymers, PE and PP, have these positive properties except perfect barrier property. Although they have sufficient moisture barrier, they are low barrier to oils and fats or other gases compared with other plastics. The high oxygen transfer rate of polyolefin is considered as their drawback that would cause poor protection of sensitive foods and beverages such as meat or milk.
Thus common films should be combined with other suitable polymers by co-extrusion, blending, lamination or coating to achieve properties that the components could not provide alone. It is more common to apply co-extrusion (blown film, cast film) to provide multilayered structure containers with various plastics.
The common polar resins using as oxygen barrier layer in food packaging are PET, PA and EVOH. The oxygen transmission rate and water vapor rate of common polymers are compared in Fig.2
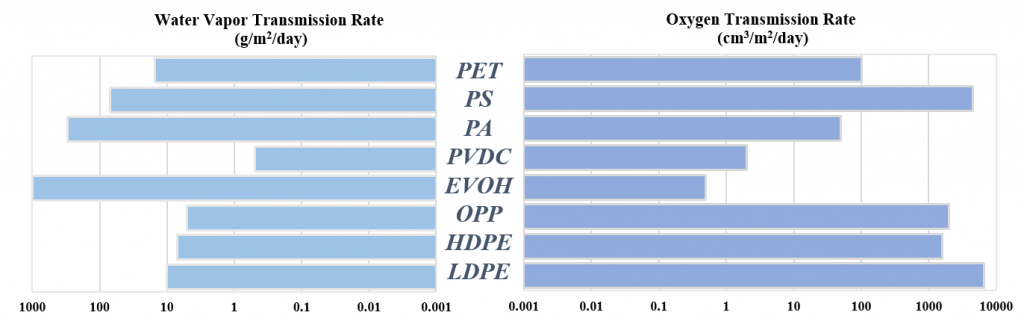
( Data from Plastics in Food Packaging by Mark J. Kirwan, et al. 2011 )
Considering transparency, processability, recyclability, cost and barrier quality, poly (ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol), EVOH, is more practical compared with others. Particularly, as vinyl alcohol content is increased in EVOH, the better oxygen barrier property is achieved. Similar Fig.3, polar polymers (EVOH) as core layer can be sandwiched between layers of polyolefin polymers (LDPE) as skin layers to improve oxygen barrier property and cover their weakness. The use of this material is remarkable somehow that the ability of 1 mm EVOH is as the same as 10 m Polyethylene.
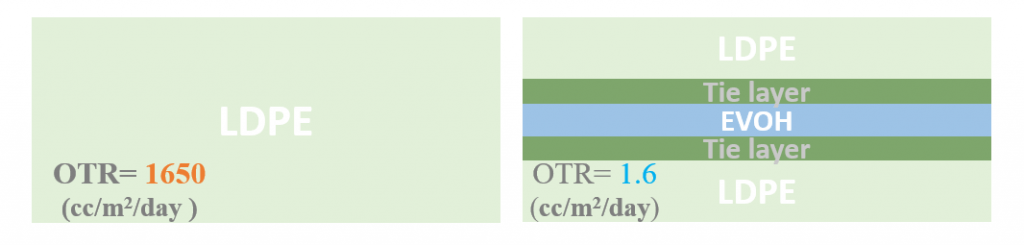
(Data from kuraray in world packaging congress 2015)
But PA or EVOH are not able to adhere to common plastics such as PE and PP. The detail information for adhesion between various polymers is shown in table 1.
Table 1. Adhesion between various polymers
| polymer | HDPE | PP | PS | PA | EVOH | PVDC |
| LDPE | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| LLDPE | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| EVA | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ |
| PE-g-MAH | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
(Data from PE-Based Multilayer Film Structures by Thomas I. Butler, et al. 2016)
This means that the main challenge in multilayer films is adhesion quality between layers. The film performance will be perfect when the incompatibility of the layers has been eliminated. The high difference in polarity cause poor interfacial adhesion. Therefore, there is necessary to apply intermediate layer to make bonds between incompatible layers. Consequently, the new type of adhesives as adhesion promoters or tie layer resin are designed with bimodal functionality to dictate compatibility to different layers. Adhesion mechanism in tie layer would differentiate it with other types of adhesives. According to Fig.4, the functional groups in tie layer cause the chemical interaction (covalent or hydrogen bond) at polar substrate-adhesive interface. Also polymer backbone in tie layer can interact with non-polar resin melt.
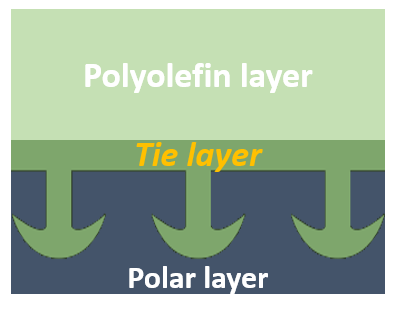
So based on chemical interaction mechanism, tie layer adhesive can either be the reactive or non-reactive. According to Fig.5, tie layer with enough thickness can improve the adhesion (peel strength) of multilayers films.
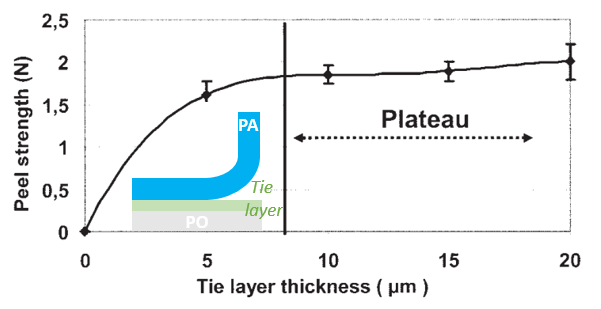
(Data from Optimization of PE/Binder/PA Extrusion Blow-molded Films by C. Poisson, et al. 2015)
The composition materials and processing parameters which can influence on adhesion quality during coextrusion, are mentioned at the table 2. For example, increasing the contact time usually increases adhesion since there is a longer time for the chemical reaction and chain entanglement to occur. On the other hand, orientation in processing cause reduction in adhesion.
Table 2. Effective factor on adhesion quality
| Adhesion ↑ | thickness | Functionality | Contact time | Temperature |
| Adhesion ↓ | Orientation | Line speed | blow-up ration | Thermoforming draw ratio |
There are various arrangement in structure of multilayer films based on protection requirement for food material. Some examples are mentioned in table 3.
Table 3. Multilayer barrier film for food materials
| PP/Tie layer/EVOH/Tie layer/PP | Bottle (Ketchup, Mayonnaises) |
| HDPE/Tie layer/EVOH/Tie layer/EVOH | Orange juice |
| HDPE/Tie layer/EVOH | Solvents |
| LDPE/Tie layer/PA/Tie layer/LDPE | Food |
| PS/Tie layer/EVOH/Tie layer/PE | Yogurt |
| PA/Tie layer/LDPE | Meat |
| LDPE/Tie layer/PA/Tie layer/LDPE | Cheese |
So end use should be considered in tie layer selection materials. The adhesive composition should be designed based on film substrates, physical requirement, and cost efficiency. Also tie-layer adhesives should have a sufficient balance of clarity and adhesion.
Aria Polymer company is manufacturer of tie layer adhesives based on your requirements.